Calcium filler masterbatch is present in various plastic products, implying its important role in the industry. Many manufacturers use this material to enhance the quality and functionality of the final items.
However, problems may occur during the production process, requiring manufacturers to pay attention and seek appropriate solutions.
This article will analyze each issue and ways to address it. Follow along!
1. Main Problems You Will Meet When Processing Calcium Filler Masterbatch
Here's a list of the main issues that may happen during the process of applying calcium filler masterbatch.
1.1. Dissimilarity and Un-uniformity of Surface
Manufacturers often prioritize the appearance of their finished masterbatch, and it is essential to develop a standard formula before production. Broken granules may result from dissimilarity and homogeneity caused by a high compound CaCO3 level in the masterbatch. Variables like unsteady temperatures, unstretched material feed, and insufficient screening of undesirable component CaCO3 granules can impact extruder machine operations. Thus, the calcium carbonate particles must be completely coated in order to guarantee homogeneous dispersion in the base polymer.
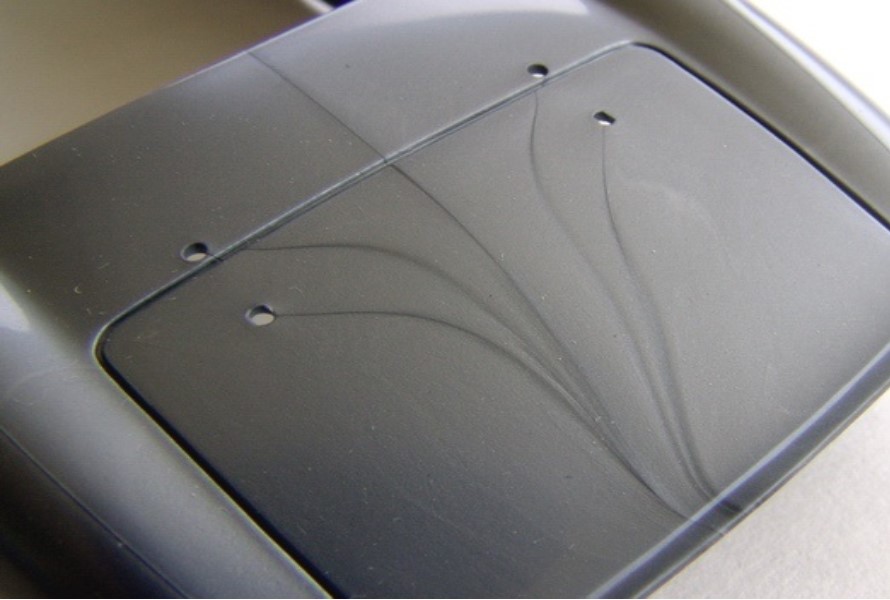

Plastic surface defect
Plus, when calcium carbonate aggregates during production, the result can be a lot of white spots or hard white particles on the film and, in extreme situations, a "foggy" look. In order to lessen the chance of agglomeration, manufacturers should apply enough coupling agents to make the particle surface lipophilic and avoid excessive friction during surface treatment. It will reduce the likelihood that the film may develop hard white particles or a lot of white blotches.
1.2. Scratches on the Surface
The products' surfaces will probably be scratched due to friction created by the materials' interaction with the extruder machine's cylinder. The solution to this issue is to apply a tiny layer of lubricant to the cylinder's inner surface, where it comes into touch with the CaCO3 combination.
The extrusion hole is another factor contributing to this problem. As a result, workers should routinely inspect the machine, paying particular attention to the extrusion hole.
1.3. Broken or Torn Film
Uneven compound CaCO3 dispersion in processing calcium filler masterbatch may lead to damaged plastic film during the laminating or blowing operations. It also makes the filter stuck, requiring replacement. Many factors cause this poor dispersion, such as high humidity, low processing temperature, low-quality processing machines, etc.
Controlling all processing stages, including examining their properties, temperature, and humidity, is essential to resolving the problem. If the quality of the materials cannot be guaranteed, it is best to switch to a different type. Before mixing, both machines and materials should be dried, and workers should adjust the machine setup if the temperature is too low, too high, or unstable.
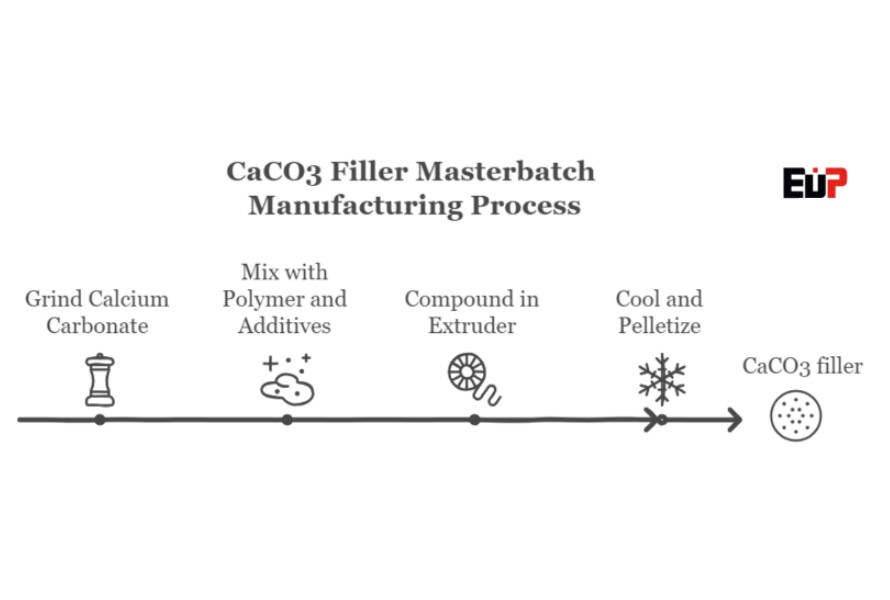
Calcium filler masterbatch manufacturing process
1.4. Extruder Option
Extruders are also crucial for granulation and material mixing. While reciprocating single-screw extruders are super-production, co-rotating twin-screw extruders are considerably superior to single-screw extruders with mixing sections. The co-parallel twin-screw extruder is less effective than the film-level filling masterbatch that uses fine, heavy calcium due to the primary raw ingredient.
The lack of calcium carbonate surface treatment in the high mixer and the first mixing with the carrier resin can be compensated for by the mixing and granulating equipment. As a result, choosing and setting up the threaded sleeves, as well as the manual extrusion mixing and granulating equipment, are equally important.
1.5. Cooling Method
Because the granulation phase involves physical labor and material responsibility, the strip water cooling operating mode should be avoided. An air-cooled die face hot cutting method is appropriate when polyethylene resin is utilized as the carrier resin. When combining matrix resin particles during film blowing, wafers with a diameter of 3 to 5 mm and a thickness of roughly 1 mm are appropriate. Blending with the substance is made easier by rapid melting.
The head of the air-cooled die face is hard to regulate; the particles are not cooled down, and they stick when the extruder has a big diameter and an output of more than 300 kg/h. For the manufacturing of modified special materials or filler masterbatch, the belt cooling approach is recommended, yet it requires a larger site and a long cooling distance.
2. Conclusion
Processing calcium filler masterbatch can present several challenges. Manufacturers should be aware of this and prepare proper solutions to ensure product quality.
The basic way to tackle issues is to create a careful formation, follow accurate processing parameters, and use the right equipment. Plus, observation is always needed to avoid unwanted problems.
3. About EuroPlas' Filler Masterbatch
If you're looking for a filler masterbatch for products, EuroPlas is glad to introduce its collection. With nearly 20 years of experience, we are a trusted partner with businesses in almost 100 countries across Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Europe.

Filler masterbatch from EuroPlas
Our filler masterbatch is designed to reduce costs and increase the qualities of the final product, such as hardness, impact resistance, stability, and printability. It is ideal for the manufacturing of PVC pipes, plastic frames, blow molding, injection molding, packaging, and door production.
We offer:
Contact us for more details!