Understanding the density of a plastic is crucial for manufacturers to optimize material selection and production processes. This article delves into the definition of plastic density, presents a comprehensive table of common plastics, and highlights the vital role density plays in the plastic industry. By grasping these concepts, professionals can enhance product quality and performance, ensuring sustainable practices in their operations.
1. What Is the Density of a Plastic?
Density is a fundamental property that measures the mass per unit volume of a material, denoted by the Greek letter ρ (rho). The formula for calculating density is:
Where ρ represents density, m is the mass, and V is the volume. In the context of plastics, density is typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), although it can also be represented in other units such as kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or pounds per cubic foot (Ib/cu ft).
To determine the density of a plastic, you have two primary methods at your disposal. The first method involves testing solid plastic in water, which is the more common approach and can be easily conducted with plastic sheets. This method allows for straightforward observation of whether the plastic floats or sinks, providing immediate insight into its density relative to water.
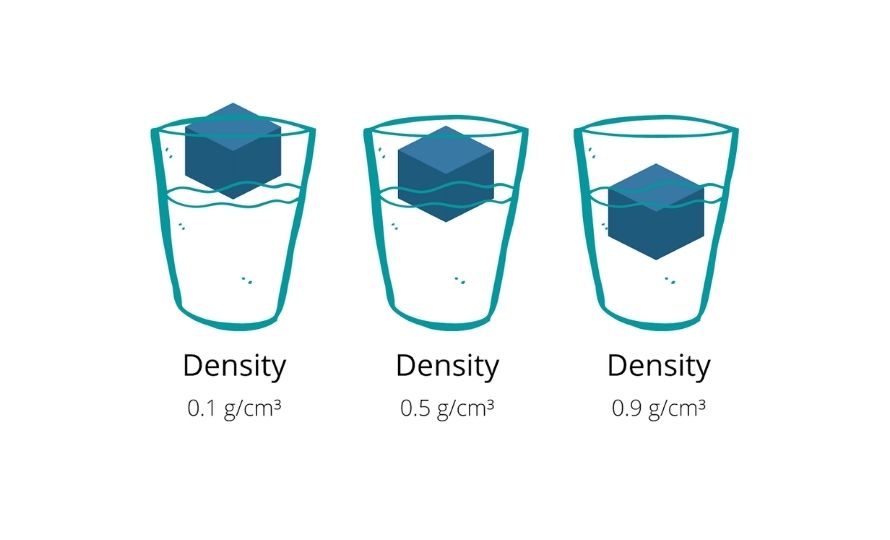
The second method entails testing the solid plastic in a liquid other than water. This alternative can be particularly useful for plastics that may react with water or for achieving more precise density measurements in specific applications. By utilizing different liquids, manufacturers can better differentiate between materials with similar densities.
The density of a plastic significantly depends on its chemical composition and structure. For instance, low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has a density of approximately 0.91 to 0.93 g/cm³, while high-density polyethylene (HDPE) ranges from 0.94 to 0.97 g/cm³. This variation in density is crucial for determining the suitability of a plastic for specific applications, particularly in industries such as woodworking and manufacturing.

2. Density Table of Some Common Plastics
The density of plastic materials is a crucial factor in various applications, influencing their performance and suitability for specific uses. Below is a table summarizing the densities of some common plastics:
These density values can vary based on factors such as temperature, processing conditions, and the presence of additives or fillers. Understanding the density of a plastic is essential for selecting the appropriate material for various applications, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness
3. The Role and Importance of Density in Plastic Industry
Density plays a crucial role in the plastic industry, influencing various aspects of material selection, processing, and application performance. Understanding the density of a plastic is essential for manufacturers and designers for several reasons:
- Material Selection: Different plastics have varying densities, which directly affect their mechanical properties and suitability for specific applications. For instance, low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is known for its flexibility, while high-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers greater strength and rigidity. This distinction helps manufacturers choose the right material based on the requirements of the final product.
- Processing Performance: The density of a plastic plays a crucial role in determining its flowability and moldability during processing. Generally, plastics with lower density exhibit superior flow characteristics, which facilitates their ability to be molded into intricate shapes. This property is especially significant in high-efficiency production environments where both precision and speed are essential for successful manufacturing outcomes.
- Cost Efficiency: Density affects the weight of plastic products, which in turn influences transportation and production costs. For example, lighter materials can lead to significant savings in shipping and handling, making them more economically viable for manufacturers. Additionally, understanding density helps in calculating the strength-to-weight ratio, which is vital for applications where weight is a concern, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- Performance Characteristics: The density of plastics also correlates with their thermal and mechanical properties. Higher density materials typically exhibit better heat resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for demanding applications. Conversely, lower density plastics may offer advantages in flexibility and impact resistance, which are desirable in packaging and consumer goods.
- Quality Control: Accurate density measurements are essential for quality assurance in plastic manufacturing. Variations in density can indicate inconsistencies in material composition or processing conditions, which can affect the performance and durability of the final product. Regular density testing helps ensure that products meet specified standards and performance criteria.

4. Conclusion
In summary, understanding the density of a plastic is crucial for optimizing their applications across various industries, including woodworking and manufacturing. By knowing the specific density values of different plastic types, manufacturers can make informed decisions regarding material selection, processing techniques, and product design. This knowledge not only enhances product performance but also contributes to efficient production practices, ensuring that the right materials are used for the right applications. As the plastic industry continues to evolve, the importance of density as a key property will remain central to innovation and sustainability efforts.
5. About EuroPlas
EuroPlas provides advanced engineering plastic compounds specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of various applications, such as automotive parts, household appliances, and electronic components. Our compounds, crafted from high-quality base resins like ABS, PC, and PBT, are enhanced with specialized additives and reinforcements to achieve optimal technical properties, including ideal density for enhanced performance and durability. By choosing EuroPlas, you select a solution that integrates flexibility, high quality, and functionality into a single material. Our product range includes PBT GF-FR compounds, PA6 and PA66 blends, flame-retardant PC compounds, fiberglass-reinforced ABS, and anti-static ABS compounds, all designed to ensure efficient operation in their intended environments.

For tailored solutions that enhance your product's performance and meet specific density requirements,
contact us today to discover how EuroPlas can elevate your manufacturing processes and product quality.