
Thermosetting plastic is one of the materials that brings many benefits
Thermosetting plastic is one of the materials that brings many benefits in terms of performance and economic efficiency to both investors and consumers. The outstanding properties of thermosetting plastics are their outstanding hardness and heat resistance. In addition, thermosetting plastics have a lot of important information that you need to update today. Understanding the properties of thermosetting plastics also contributes to environmental protection through proper use of this material. It will be quite surprising to know that thermoset plastic can be reused, all will be detailed to you right below!

Thermosetting are formed through a three-dimensional transformation process
Thermosetting plastic is one of the most advanced materials and is commonly used in many manufacturing industries today. Thermosetting materials are formed through a three-dimensional chemical transformation process. In its initial state, the material exists in liquid form. When subjected to increased temperature and pressure (which may be accompanied by an unpleasant odor), thermosetting plastics can be shaped into a variety of molds. Once cooled, thermosetting plastic will become extremely strong and tough. The cooled state of thermosetting plastics will be one in which they remain indefinitely. Because thermosetting plastics cannot be dissolved back to their original state, the material is considered non-recyclable. However, many industries, especially heavy industries, favor thermosetting plastics thanks to their outstanding properties.
Thermosetting plastics have quite high temperature resistant and low levels of thermal conductivity. Because of this outstanding feature of thermosetting plastics, they rarely deform during long-term exposure to high temperatures. Besides, thermosetting plastic is very durable and has a long lifespan. Thermosetting plastics are considered to be many times more durable than thermoplastics. This is demonstrated in the ability to preserve structure after use or high-intensity stretching. Thermoplastic is hard, so impact resistance is much better, helping the product minimize damage caused by external impacts. Thermosetting plastics have very good water resistance and abrasion resistance. This is one of the extremely ideal options in today's heavy industry.
Read more: Thermosetting vs Thermoplastic: Which one to choose?
2. Explanation of thermosetting plastic
2.1 Description of the polymerization process
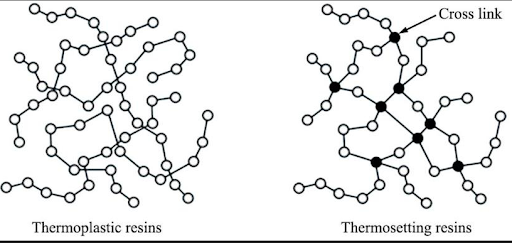
Polymerization is the linking process of monomers
Polymerization is the linking process of monomers. A monomer is a single molecule that is connected to at least two other monomers, also known as a covalent bond. As a result, after this bonding process, they will form larger molecules that we call polymers. Polymerization requires a condition that at least one of the two monomers must have a double bond. The newly created Monomers will combine to form a complete polymer with mostly irreversible cross-links. Polymer molecules will have a chain structure in the case of a monomer linked to two other molecules. In case the monomer is linked with three or more, there will be a cross bond. Besides, Polymers are divided into many groups such as polymerization polymers, condensation polymers, branched and unbranched polymers. In particular, polymer molecules can also form a three-dimensional network structure. Below are some common polymer preparation processes:
Polymerization reactions combine multiple monomers of the same substance to form a polymer. The reaction equation is:
nCH2=CH-CH=CH2 → (-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-)n
Butadiene polymerization reaction 1,3
The condensation reaction combines many monomers to form a polymer and a byproduct mainly water (requiring the monomer to be able to split water). The reaction equation is:
n H-NH-(CH2)5-CO-OH → (-NH-(CH2)5-CO-)n + nH2O n p-HO-CO-C6H4-CO-OH + n H-OCH2-CH2O-H → (-CO-C6H4-CO-OCH2-CH2O-)n + 2nH2O
Polymerization - combination reaction
2.2 Formation of a three-dimensional network structure
As mentioned above, Polymers can have a branched structure or an unbranched structure. Besides, typical is the formation of three-dimensional structure. Mo-no-mers can combine two or more single molecules. In the case of bonds of three or more molecules, a three-dimensional structure will form. The condition for the formation of a three-dimensional structure is that one of the molecules must have a double bond.
2.3 Irreversible Cross-Linking
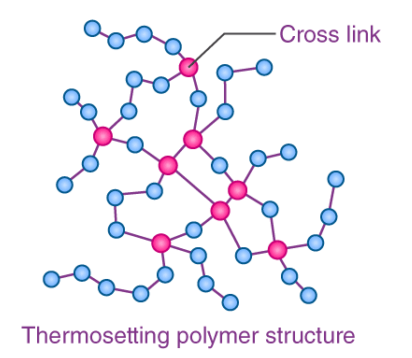
Cross-links can have a greater strength than the bonds between carbon atoms
In the process of linking monomer molecules, larger molecules will form and are called polymers. Cross-linking occurs when combining monomers with three or more numbers of molecules. Cross-links have equal or even greater strength than the bonds between carbon atoms of the polymer chain. These are called irreversible cross-links.
3. Lack of melting point
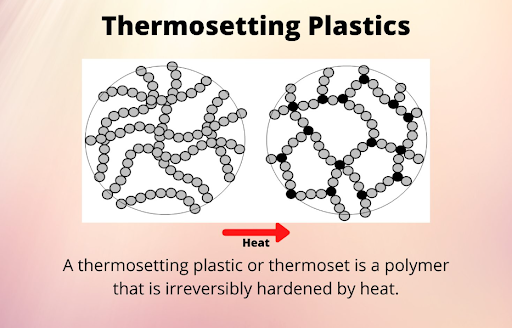
There is no reversible melting point in thermosetting plastics
In fact, plastic is used in almost every application in human life today. However, the distinction between thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics also causes a lot of confusion for users. One of the most common and easiest ways to differentiate is based on their heat resistance. We are quite familiar with thermoplastic products that can be melted and reshaped into new products. On the contrary, for thermosetting plastics this is almost not applicable. Quite famous for its excellent heat resistance, thermosetting plastics can meet the demands of prolonged contact with hot surfaces or even high-temperature boiled water. However, the second melting process applied to thermosetting plastics can cause excessive destruction of this material. This means that thermosetting plastics cannot be melted and remolded like thermoplastics.
In terms of thermodynamic processes, the process can be carried out in one of two ways: reversible or irreversible. For thermosetting plastics, there is no reversible melting point for this material. In thermodynamics, it can be understood that the molecules in thermosetting plastics are not capable of being reversed by changes from changes in the surrounding environment. For example, increasing pressure or increasing temperature cannot change the molecules in a positive direction but can cause destruction. The absence of a reversible melting point in thermosetting plastics is also an important note for manufacturers and consumers.
4. Challenges in recycling
4.1 Optimal solution in recycling thermosetting plastics

Thermosetting plastics can be reshaped and reused for many other applications
Nowadays, the importance of environmental protection is increasingly enhanced around the world. This causes thermosetting plastics to face certain challenges because their recyclability is not comparable to that of thermoplastics. However, with the development of technology and the ever-expanding creativity of people, thermosetting plastics can be reshaped and reused for many other applications. Thermosetting plastics can be recycled and reshaped, so don't rush to throw away thermosetting plastic products in your home. Items made from thermosetting plastic can be shaped and redecorated to create incredibly creative plant pots. In addition, utilizing and reshaping thermosetting plastic products can also help create eye-catching decorative items in your home.
4.2 How to reshape hard plastic

Thermosetting plastics can be recycled and reshaped
Thermosetting plastics are inherently hard and durable, so they will be a worthy choice for applications that require high durability over the years. To shape this type of material, which is quite hard, you need to consider choosing tools with relatively low cutting capacity such as a handsaw or chainsaw instead of a knife to save effort. Adjusting the shape and size of hard plastic will no longer be too difficult with these support tools. In addition, you can consider choosing options that combine thermosetting plastic with other recyclable hard plastics (e.g. HDPE, LDPE, PVC, etc) to contribute to environmental protection.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, thermosetting plastic is one of the prominent materials in manufacturing industries and especially heavy industry. Thermosetting plastic gives users a product that is durable over time and saves significant maintenance effort. Thanks to irreversible bonds, the hardness of thermosetting plastics is increasingly improving, but this causes limitations in reuse. Read more useful articles about materials at EuroPlas today! We are always proud to be a reliable source of information for your project.